Article
What Is the Stock Market, What Does It Do, and How Does It Work?
The stock market is a financial marketplace where individuals and institutions can buy and sell shares of publicly traded companies. It is a crucial component of the global financial system and plays a vital role in the economy by facilitating the flow of capital and providing a means for companies to raise funds for expansion and growth.
Here's an overview of how the stock market works:
-
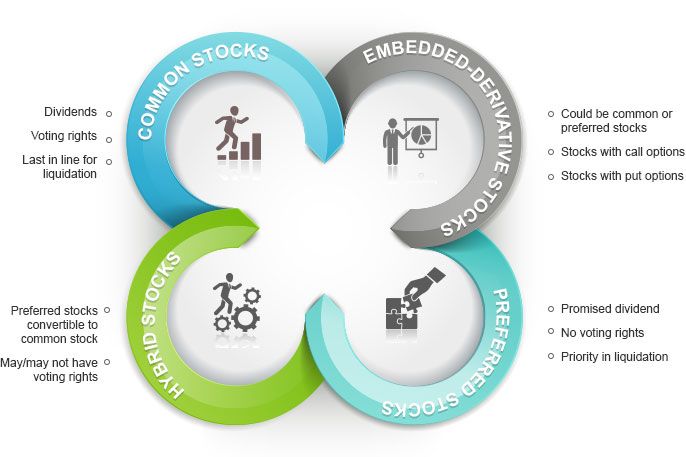
Publicly Traded Companies: Companies that wish to raise capital from the public can do so by issuing shares of ownership in the form of stocks. These shares represent a portion of the company's ownership and entitle the shareholders to a proportional claim on the company's assets and earnings.
-
Initial Public Offering (IPO): When a company decides to go public and issue shares for the first time, it conducts an Initial Public Offering (IPO). During the IPO, the company offers a certain number of shares to the public and sets an initial price for each share.
-
Stock Exchanges: The stock market consists of various stock exchanges, such as the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and NASDAQ in the United States, London Stock Exchange (LSE) in the UK, and Tokyo Stock Exchange (TSE) in Japan. These exchanges act as marketplaces where buyers and sellers can meet to trade stocks. They provide the infrastructure and regulatory framework for trading activities.
-
Brokers and Online Trading Platforms: Individual investors and institutions typically use brokers or online trading platforms to buy and sell stocks on the stock exchanges. Brokers facilitate the trades by matching buyers with sellers and executing the transactions.
-
Stock Price Determination: The price of a stock is determined by supply and demand in the market. If more people want to buy a stock (demand) than sell it (supply), the price will generally rise. Conversely, if more people want to sell than buy, the price will likely fall.
-
Market Indices: Stock market indices, such as the S&P 500, Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA), or FTSE 100, represent a basket of stocks that are used to gauge the overall performance of the market or specific sectors.
-
Trading Hours: Stock exchanges have specific trading hours during which trading can occur. Typically, they are open for several hours during weekdays and closed on weekends and holidays.
-
Long-Term Investing and Speculation: Investors can buy stocks with the intention of holding them for the long term, aiming to benefit from the company's growth and dividends. Speculators, on the other hand, may buy and sell stocks over short periods, attempting to profit from short-term price fluctuations.
-
Market Regulation: Stock markets are subject to regulation by government agencies, such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in the United States, to ensure fair and transparent trading practices and protect investors from fraud or manipulation.
It's important to note that investing in the stock market carries inherent risks, and stock prices can be volatile. Investors should conduct thorough research, diversify their portfolios, and consider their risk tolerance before participating in the stock market.